Hello and welcome to our blog! In the world of electronics, selecting the right components can sometimes feel overwhelming, given the vast array of choices available. However, some components are so integral to the functionality of electrical systems that their importance is often overlooked. One such component is the electrical terminal. These small, seemingly simple devices play a crucial role in ensuring secure, reliable, and efficient electrical connections in circuits.
Whether you’re working on automotive repairs, assembling computer systems, or designing industrial machinery, the right electrical terminal ensures smooth and uninterrupted current flow, which is vital for the performance and longevity of your devices. In this post, we’ll delve into the top 10 types of electrical terminals, their specific applications, and the factors you should consider when selecting the best terminals for your projects.
What is an Electrical Terminal?
An electrical terminal is a connection device used to join electrical wires to other components, such as connectors, studs, or other wires, to ensure an uninterrupted flow of current through the circuit. These terminals come in various materials, shapes, and designs to suit different functions, from providing power to facilitating data transmission. Electrical terminals are essential across several industries, including automotive, industrial manufacturing, consumer electronics, and telecommunications.
Choosing the right terminal for the job is critical for ensuring safety, minimizing errors, and improving the reliability of the overall system. This guide will help you understand the top types of terminals, their advantages and limitations, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
1. Ring Terminals
Applications and Features:
Ring terminals are among the most reliable and widely used types of electrical connectors. They feature a metal ring that fits securely over a stud or screw, making them ideal for high-vibration environments where a stable connection is needed. They are used in applications like automotive battery wiring, alternators, and industrial machinery where a durable connection is crucial.
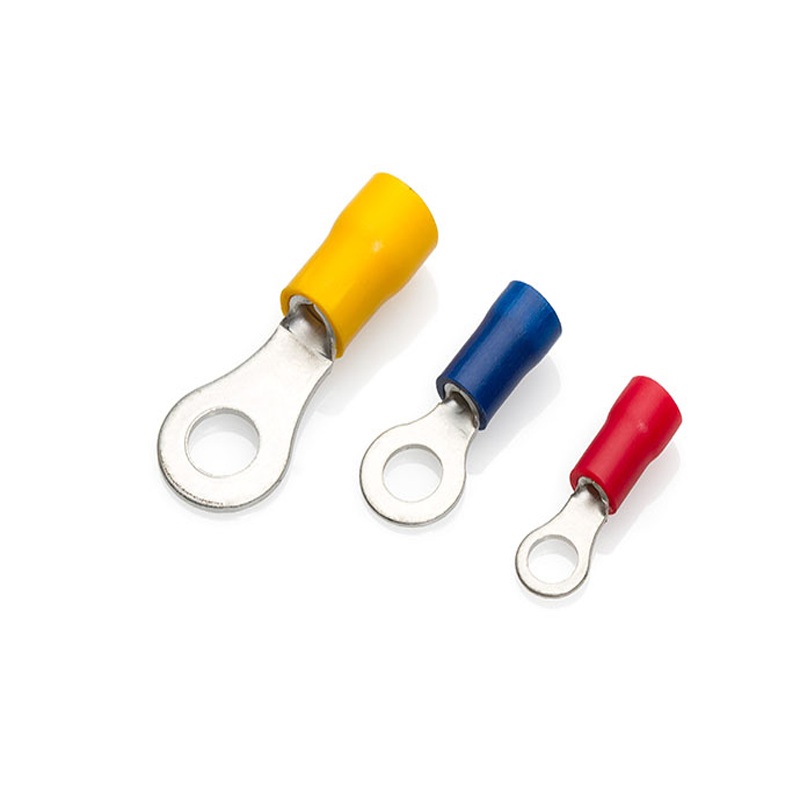

Advantages:
Ring terminals offer a strong, permanent connection that resists loosening over time. Once installed, they ensure that electrical contact remains stable even in high-stress applications.
Limitations:
While highly secure, ring terminals require a stud or screw for installation and may not be suitable for spaces where such fasteners are unavailable. Also, they are less ideal for applications requiring frequent disconnections.
2. Spade Terminals
Applications and Features:
Spade terminals (also known as fork terminals) are designed to connect easily to screws or studs. Their unique fork-like design allows them to be attached or detached without removing the fastener, which is ideal for situations where connections need to be made or broken frequently.
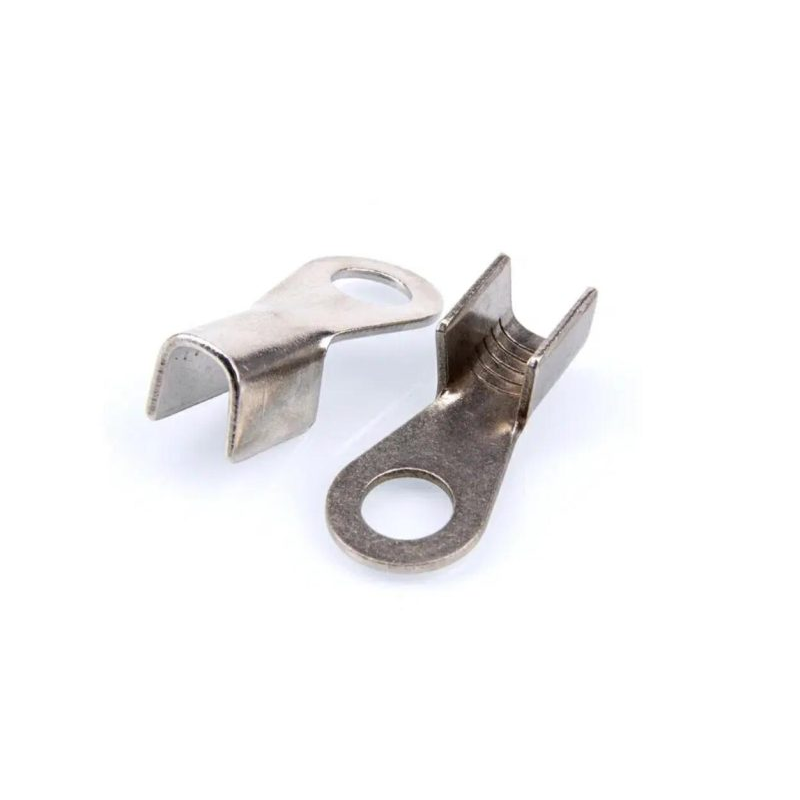

Advantages:
They are easy to install and remove, making them great for automotive wiring and applications where maintenance or troubleshooting is required. Spade terminals are available in both insulated and non-insulated variants, giving flexibility depending on the environment.
Limitations:
These terminals are less secure than ring terminals and can be prone to slipping off in environments with excessive vibration.
3. Butt Connectors
Applications and Features:
Butt connectors are used to join two wires end-to-end in a secure, inline connection. These connectors are frequently used in tight spaces where splicing wires is needed, especially in automotive and marine applications.
Advantages:
Butt connectors provide a reliable, neat connection, particularly when crimped correctly. The insulation adds an extra layer of protection against short circuits.
Limitations:
They are generally not suitable for high-current applications as the connection could degrade over time under excessive load.
4. Bullet Connectors
Applications and Features:
Bullet connectors feature a cylindrical design that slides into a matching socket for a secure yet easily detachable connection. They are popular in applications where components need to be connected or disconnected quickly, such as automotive and marine systems.
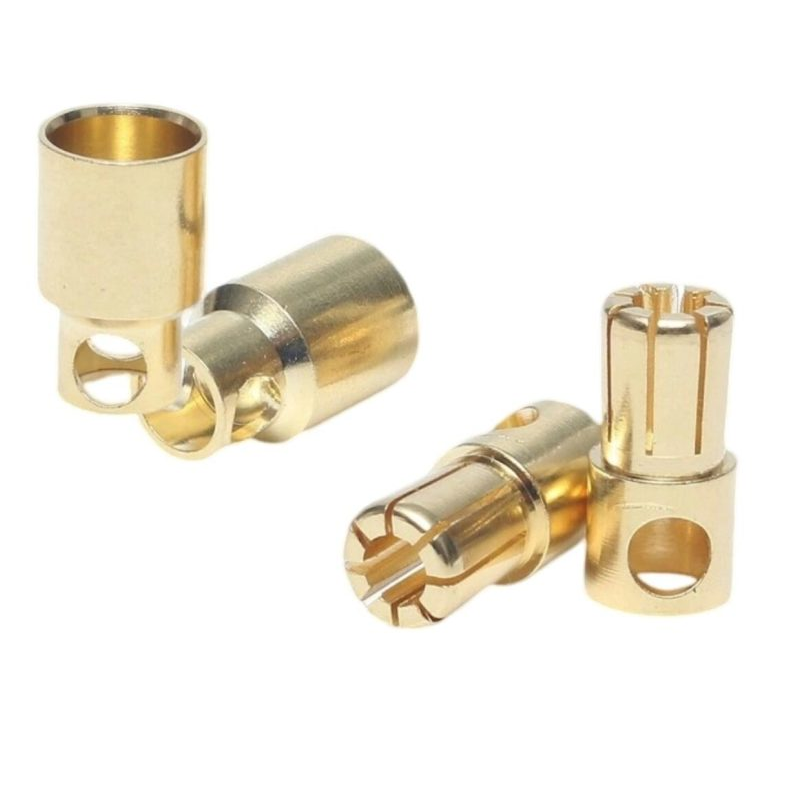

Advantages:
Their quick-disconnect nature allows for easy installation and removal, making them perfect for systems requiring frequent disconnection.
Limitations:
Bullet connectors are typically used for low-to-medium current applications and may not be robust enough for high-power systems.
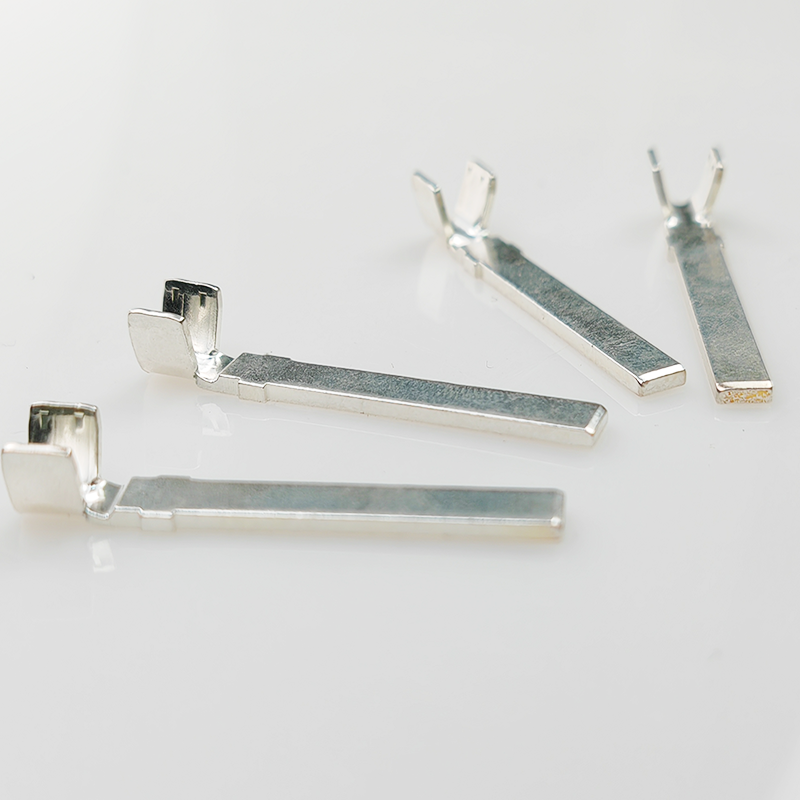
5. Flag Terminals
Applications and Features:
Flag terminals have a unique right-angle design that allows for a space-efficient connection in tight, confined spaces. They are particularly suited for use in consumer electronics, such as televisions and computers, where organizing the wiring layout is crucial.
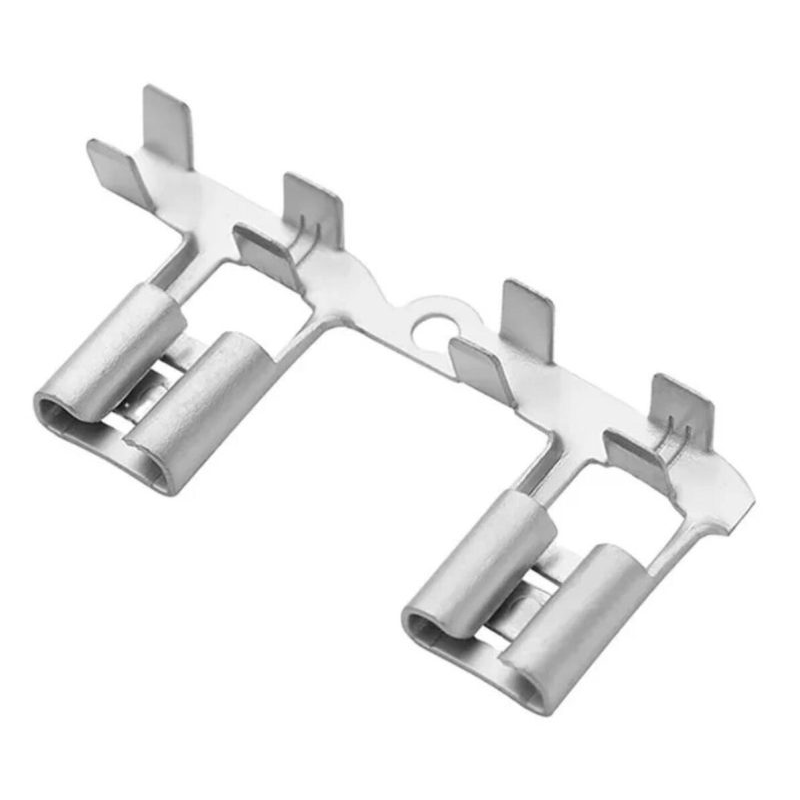

Advantages:
Their compact design makes them ideal for applications where space-saving is a priority. The perpendicular structure helps keep wiring organized and neat.
Limitations:
Their specialized design may limit their use in some applications, and they may not provide as secure a connection as other terminal types, particularly in high-vibration environments.
6. Pin Terminals
Applications and Features:
Pin terminals are used to establish connections in terminal blocks and connectors. Their pin-like design ensures reliable and secure contact, making them perfect for complex systems with multiple wire connections.
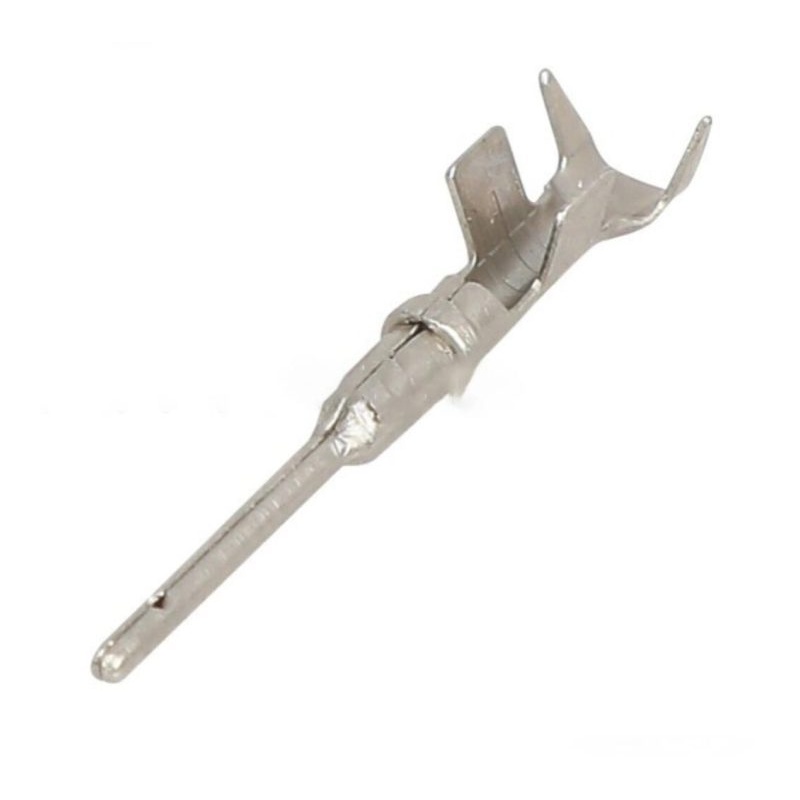

Advantages:
Pin terminals simplify wiring in control systems and circuit boards, reducing the risk of shorts. They are also highly reliable, especially in vibration-prone environments.
Limitations:
While reliable, pin terminals may not be suitable for high-current applications and require careful installation to avoid connection issues.
7. Fork Terminals
Applications and Features:
Fork terminals have an open-ended design, making them easy to attach or detach from screws or studs. They are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications, where frequent disconnection is needed.
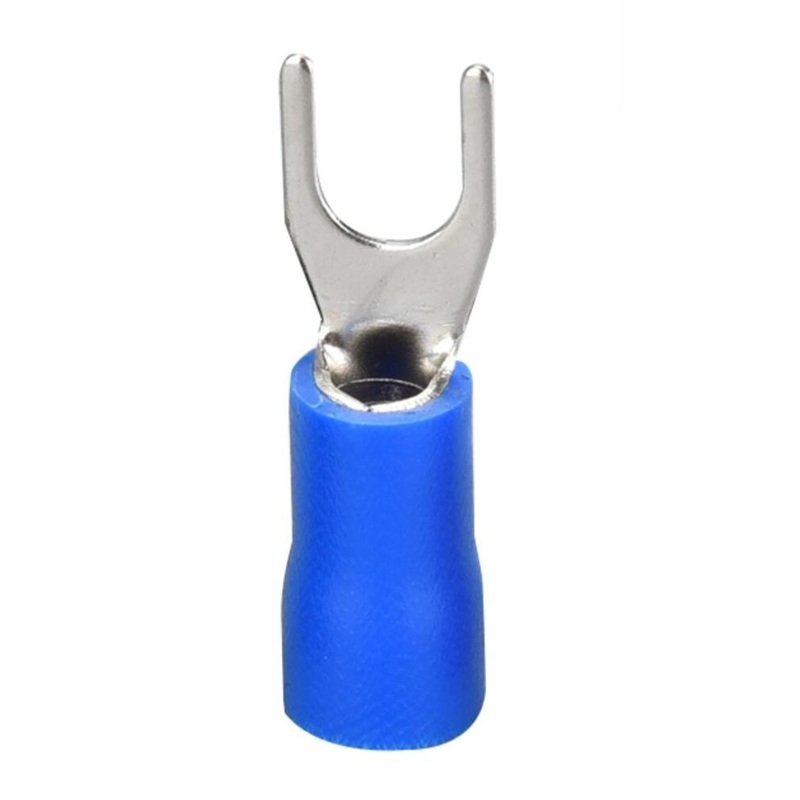

Advantages:
They provide a reliable, secure connection and are easy to install. The open-ended design allows for quick adjustments, which is helpful for applications requiring regular maintenance.
Limitations:
Fork terminals do not offer the same level of security as ring terminals, and they may not perform well in environments with high levels of vibration.
8. Quick-Disconnect Terminals
Applications and Features:
Quick-disconnect terminals feature a male and female component that easily snaps together, making them perfect for systems that require frequent connections and disconnections. They are typically used in automotive, marine, and industrial applications.
Advantages:
The primary advantage of quick-disconnect terminals is their tool-free, fast connection, which is essential in systems requiring frequent maintenance or part replacement.
Limitations:
These terminals are suitable for low-to-medium current applications but may not be durable enough for high-power systems.
9. Wire Nuts
Applications and Features:
Wire nuts are twist-on connectors used to join multiple wires together securely. They are most commonly used in household electrical systems, where multiple wires need to be securely joined.
Advantages:
Wire nuts are incredibly easy to use and provide reliable connections. The twist-on mechanism ensures a tight and insulated connection.
Limitations:
Wire nuts are not suitable for environments that experience extreme temperatures or moisture, as their plastic casings can degrade over time.
10. Insulated vs. Non-Insulated Terminals
Applications and Features:
Insulated terminals feature a protective layer that shields the metal part of the terminal, preventing accidental electrical contact and reducing the risk of short circuits. Non-insulated terminals, by contrast, are more compact and are often used in environments where safety risks are minimal.
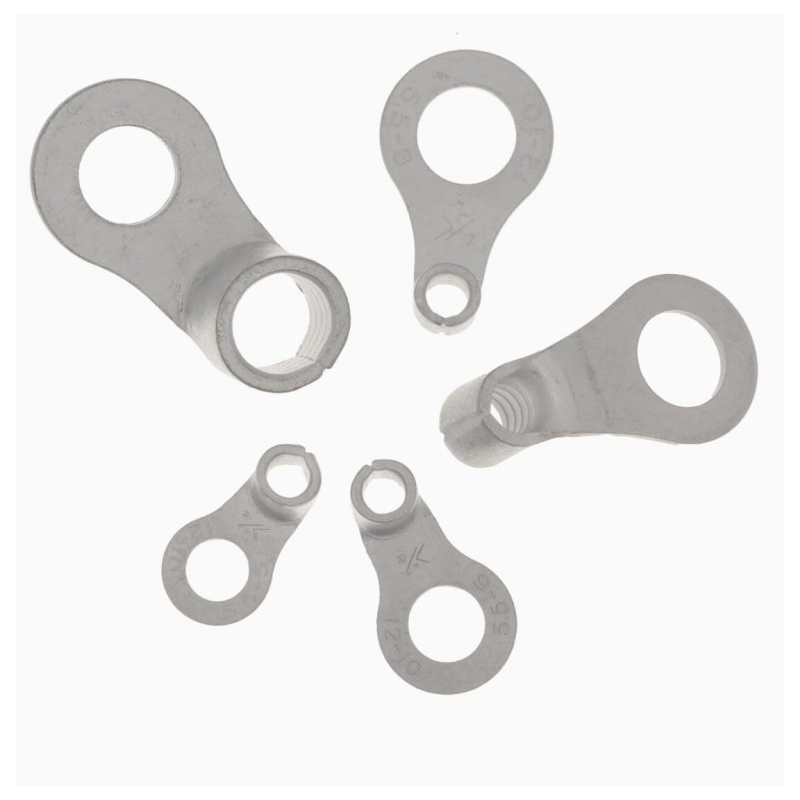

Advantages:
Insulated terminals add an extra layer of protection, making them ideal for environments where electrical safety is a concern. Non-insulated terminals are more compact and suitable for controlled environments like industrial panels.
Limitations:
Insulated terminals can be bulkier, while non-insulated variants may expose wiring to potential safety hazards.
Choosing the Right Terminal for Your Application
When selecting an electrical terminal for your project, it’s important to consider factors such as wire size, material (e.g., copper, brass, or aluminum), and environmental conditions. Whether you’re working with automotive, industrial, or consumer electronics, each application has its own set of requirements that will determine which terminal is the best fit.
Conclusion
Selecting the right electrical terminal is crucial to ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your electrical system. If you need expert guidance or high-quality terminals for your projects, Plantmetal is here to assist you. With our comprehensive selection of electrical terminals, crafted to meet the highest standards of quality, we can help you achieve secure, long-lasting connections for any application.
If you’re ready to choose the best terminals for your needs, or if you have any questions about our products and services, don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to help!Get in touch today to discuss your project needs and find the perfect solution for your electrical connections.




