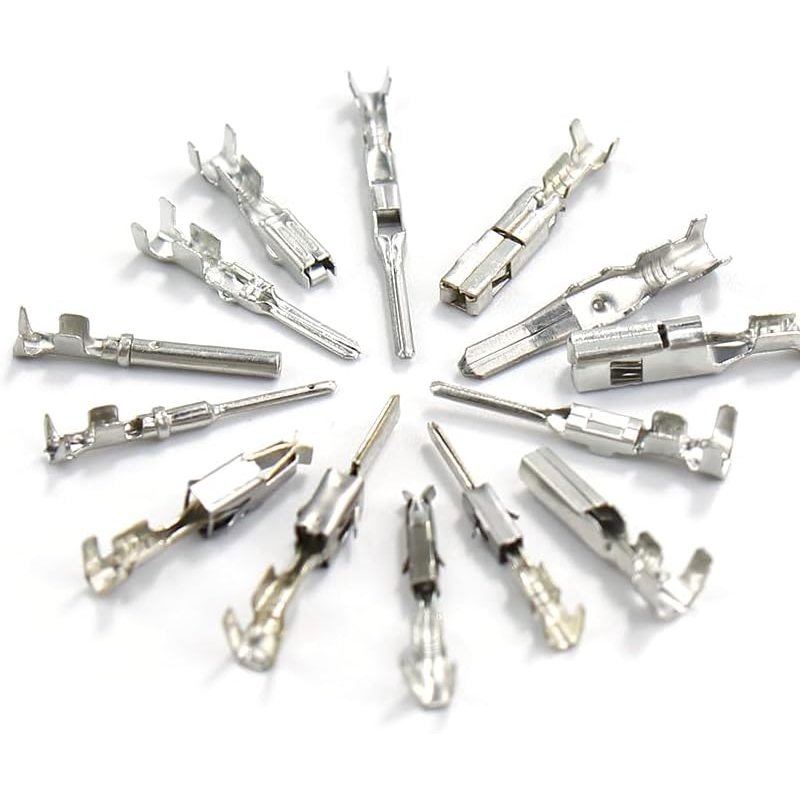
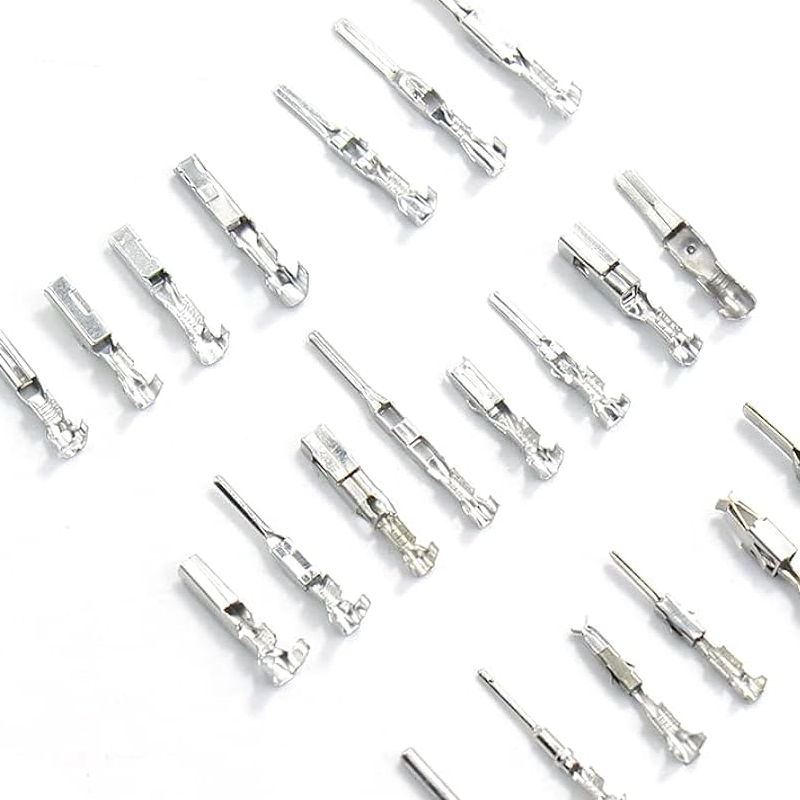
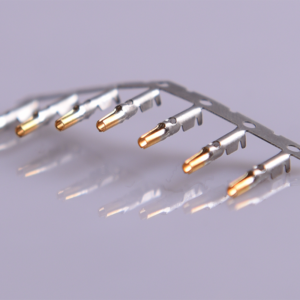
Overview:
Custom Metal Wire Connectors for Automotive Parts are essential components in ensuring secure, high-performance electrical connections within the automotive industry. Our team specializes in designing and manufacturing precision-engineered wire connectors tailored to meet the demanding requirements of automotive applications. Using advanced stamping techniques, including high-speed progressive die stamping and automated crimping processes, we produce connectors that offer superior conductivity, durability, and resistance to vibration and heat. With a focus on quality and reliability, our custom wire connectors are designed to perform under the harshest conditions, ensuring long-lasting, efficient electrical systems in vehicles. Our connectors provide the perfect solution for automotive electrical connections.
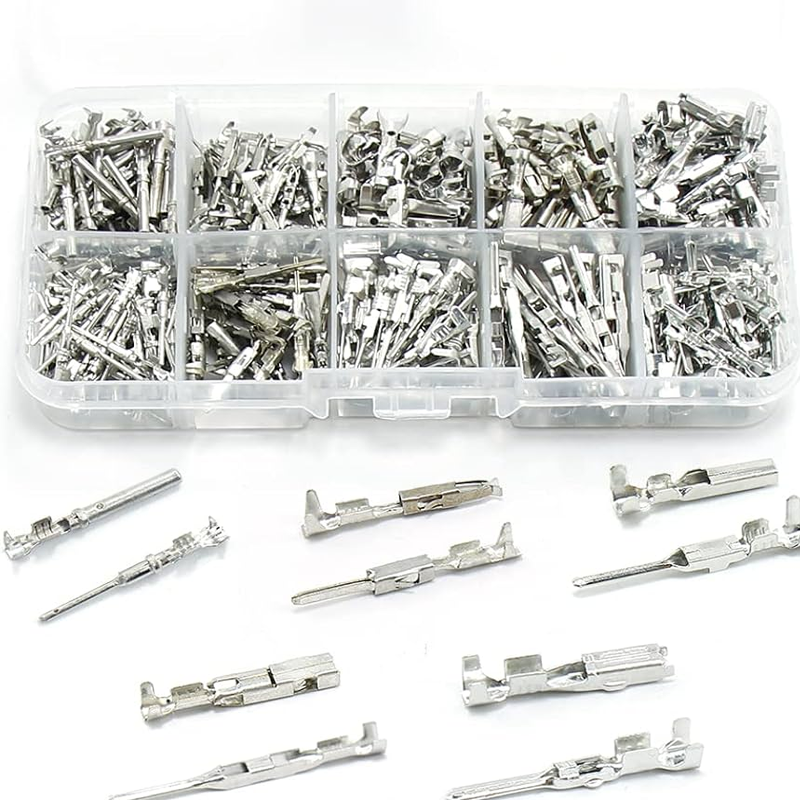

Details:
| Attribute | Details |
| Processing Type | Shaping Metal |
| Material | Copper, Stainless Steel, Aluminium, etc. |
| Mould | Multistep Progressive Dies |
| Surface Processing | Electroplating |
| Process | Fine Blanking, Multi-Position Forming Process |
| Industry | Metal Stamping Parts |
| Tolerances | 0.01 mm |
| Certification | ISO 9001 |
| Production Cycles | 7–15 Days Per Order |
| Testing | Horizontal & Vertical Flame Test, Salt Spray Test |
| Mould Leadtime | Within 20 Working Days |
| Specification | Customized |
| Origin | Xiamen, China |
| Production Capacity | 5000 PCS/Day in One Machine |
Production Process:
-
Material Selection
The first step is to select the appropriate material for the wire connector, such as copper, stainless steel, or aluminum. The material chosen must meet the specific requirements for conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion.
-
Blanking
In this step, the material is cut into flat sheets or blanks using a stamping press. The size and shape of the blanks are determined by the design specifications of the wire connector.
-
Progressive Die Stamping
This involves using progressive dies in a high-speed stamping press to progressively shape the blank into the desired form. Multiple steps are performed in a single press cycle to cut, bend, and form the connector.
-
Forming and Shaping
The connector undergoes further forming to achieve its final shape. This includes bending and forming the metal into the connector’s specific design, such as the terminals or contact points.
-
Surface Treatment
Once the connector is shaped, surface treatments like electroplating are applied to improve electrical conductivity, prevent corrosion, and enhance overall durability. Common finishes include gold, nickel, or tin plating.
-
Assembly (if applicable)
In some cases, wire connectors are assembled with additional components, such as insulation sleeves or terminals, using automatic assembly systems. This step ensures the connectors meet final design and functional specifications.
-
Testing and Quality Control
Rigorous testing is conducted to ensure the connectors meet performance and reliability standards. This may include electrical testing, dimensional checks, and environmental tests such as salt spray or thermal cycling.
-
Packaging and Shipping
After passing the final quality checks, the connectors are packaged, often on reels or in bulk packaging, for shipment. Packaging must protect the connectors from damage during transit and ensure they are ready for assembly or end use.
Surface Options
-
Nickel Plating
A process in which a thin layer of nickel is deposited onto the surface of a metal component to enhance corrosion resistance, improve durability, and provide a smooth finish.
-
Galvanization
The application of a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rust and corrosion, typically achieved through hot-dip or electrogalvanization methods.
-
Chrome Plating
A technique used to apply a thin layer of chromium onto the surface of metal parts, offering enhanced resistance to wear, corrosion, and oxidation, along with a high-gloss finish.
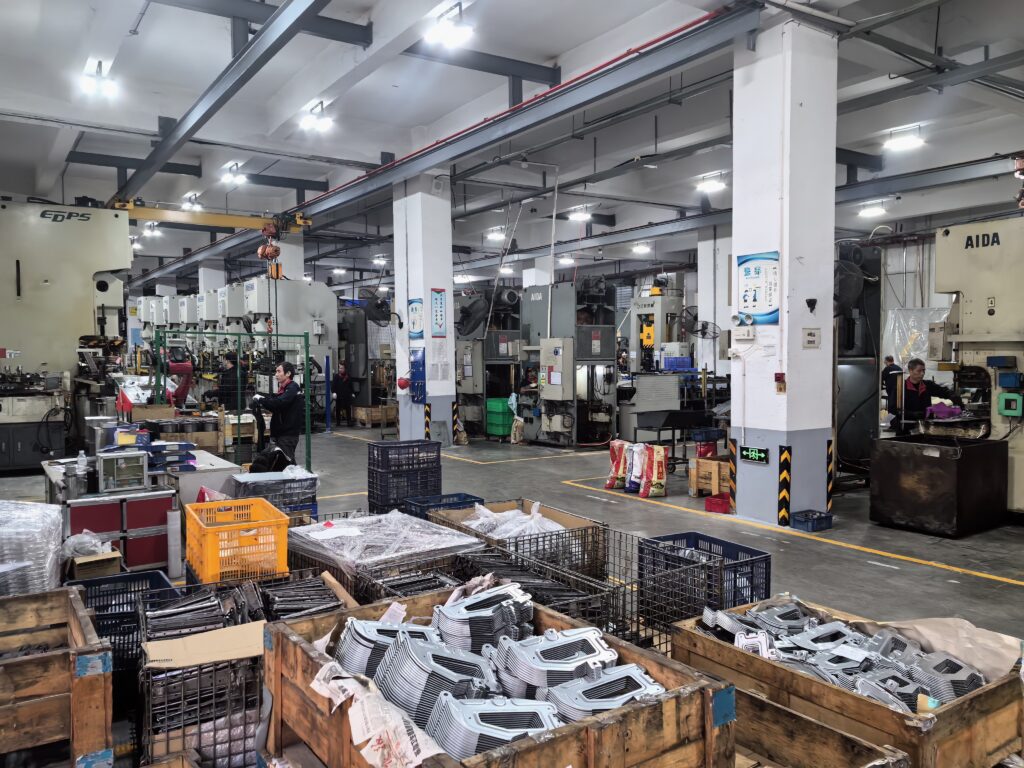
Factory Show: