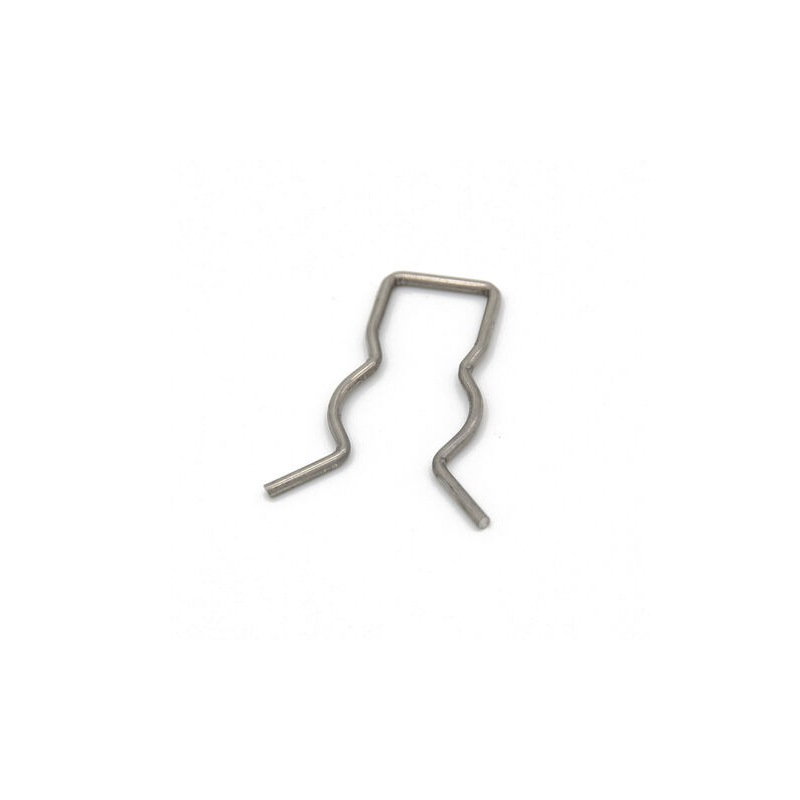
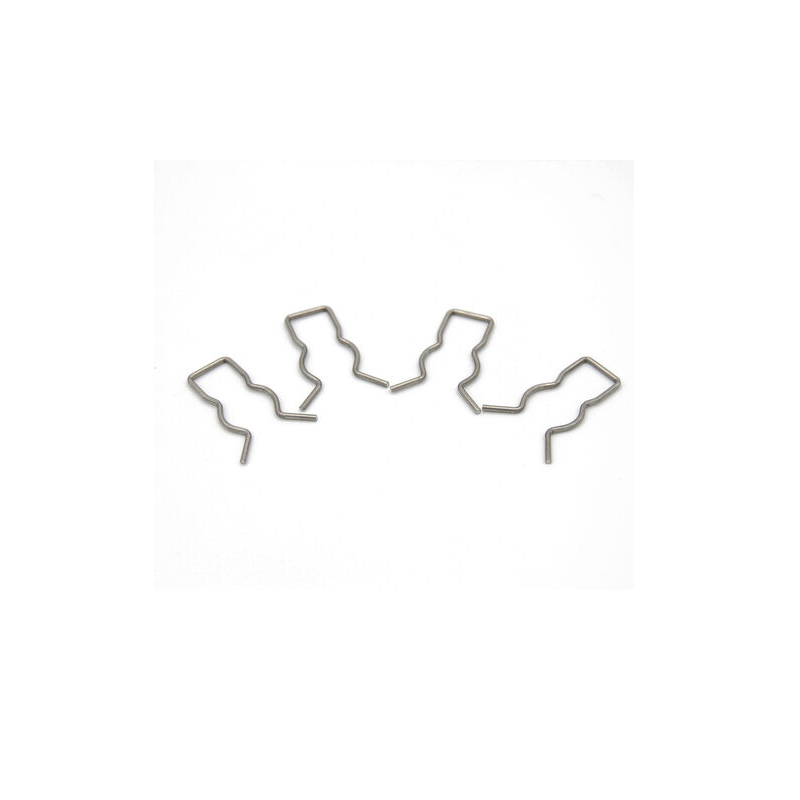
Overview
Nitinol wire forming involves shaping nickel-titanium alloy wires into precise configurations for use in various high-performance applications. Known for its unique properties such as shape memory, superelasticity, and biocompatibility, nitinol is commonly used in medical devices, aerospace components, and robotics. The wire forming process includes precision bending, coiling, and heat treatment to achieve custom shapes and maintain performance under extreme conditions. Its versatility and reliability make nitinol wire forming essential for advanced engineering and medical solutions.
Basic Information
– Surface Treatment: Electroplating
– Forming Process: Metal Stamping Parts
– Surface Finish Options: Nickel Plating, Sn Plating, Tin Plating, Zinc Plating
– Sample Availability: Available
– Tolerance: ±0.001 mm
– Size: Customizable as per requirement
– Application: Industrial, Furniture, Automotive, Motorcycle, etc.
– Manufacturing Approach: Metal Stamping, Cutting, Punching, Bending, Welding
– Transport Packaging: OPP Bag, Box, or Custom
– Specification: Customized
– Origin: Xiamen, China
Surface Treatments for Metal Stamping Parts
-
Electroplating
– Description: A process that deposits a layer of metal onto the surface of the part using an electric current. Commonly used for improving corrosion resistance and enhancing appearance.
– Types: Nickel plating, chrome plating, zinc plating.
-
Powder Coating
– Description: A dry coating process where powdered paint is electrostatically applied and then cured under heat. It provides a durable, high-quality finish with excellent resistance to scratches, chipping, and fading.
-
Anodizing
– Description: An electrochemical process that converts the surface of aluminum into a durable, corrosion-resistant layer. Anodizing also enhances appearance and can be dyed in various colors.
-
Plating
– Description: The application of a thin layer of metal to the surface of the part to improve wear resistance, reduce friction, or provide an aesthetic finish.
– Types: Tin plating, copper plating.
-
Spraying
– Description: A method where paint or protective coating is sprayed onto the part’s surface. This process is used for both aesthetic and protective purposes, offering a wide range of colors and finishes.
-
Oxidation
– Description: A chemical treatment that forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of metals, such as steel. It improves corrosion resistance and can provide a unique aesthetic finish.
-
Polishing
– Description: A mechanical process that smooths and shines the surface of the part. Polishing removes imperfections and enhances the visual appeal of the metal.
-
Sandblasting
– Description: A process that uses high-speed abrasive particles to clean or roughen the surface. It prepares the surface for further treatments or provides a textured finish.
-
Passivation
– Description: A treatment process that enhances the natural oxide layer on stainless steel to improve corrosion resistance. It involves soaking the part in a solution that removes free iron and other contaminants.
The Production Process for Our Metal Stamping Parts:
-
Order Receipt and Drawing Review
– Receive and review customer orders, including technical drawings in formats such as DXF, IGS, STEP, or PDF.
-
Design Confirmation
– Confirm design details with the customer to ensure accuracy before production begins.
-
Material Preparation
– Select and prepare metal sheets according to the required specifications.
-
Precision Cutting
– Utilize laser cutting and CNC shearing to cut metal sheets to precise dimensions.
-
Forming and Shaping
– Perform bending, punching, and stamping to achieve the desired shapes and features.
-
Welding and Riveting
– Join metal components using advanced welding techniques and riveting.
-
Surface Treatment
– Apply necessary surface treatments, including plating and spraying, to enhance durability and appearance.
-
Assembly and Quality Control
– Assemble the components and conduct rigorous quality checks to ensure adherence to specifications.
-
Packaging and Shipping
– Package finished parts securely and manage logistics for timely delivery to the customer.
-
After-Sales Support
– Provide ongoing support and address any post-delivery issues to ensure customer satisfaction.