When it comes to shaping sheet metal, two commonly used processes are metal punching and metal stamping. While these terms might seem interchangeable, each method serves distinct purposes and is suited to different types of manufacturing needs. In this article, we will explore the key differences between metal punching and metal stamping, helping you understand when to use each technique. Whether you’re a manufacturer, engineer, or designer, it’s essential to know how these processes work to optimize production efficiency, reduce costs, and avoid common pitfalls.
At Plantmetal, we specialize in both metal punching and stamping, providing customized solutions to meet the unique needs of our clients. Let’s delve into the technical distinctions and applications of these methods to help you make informed decisions for your next project.
What is Metal Stamping?
Metal stamping is a comprehensive cold-forming process that transforms flat metal sheets into precise shapes using high-pressure presses. The metal sheet is placed under a die in a stamping press, where the die and tool work together to create the desired form. While stamping can include cutting, it also covers a wide range of other operations such as bending, embossing, and flanging.
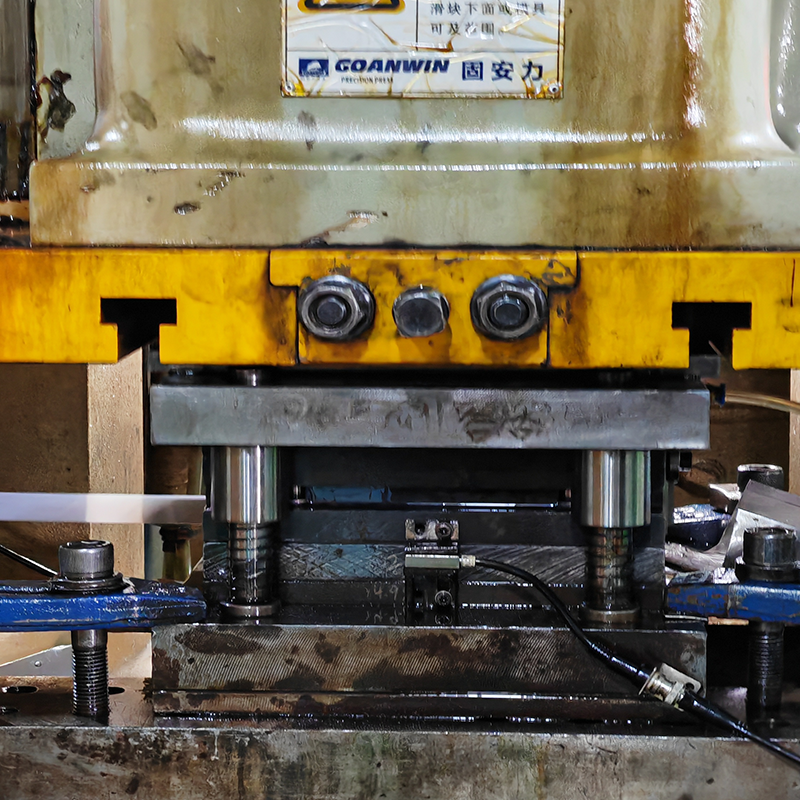

Stamping is often performed in stages, with each stage progressively shaping the metal into the final design. This process is widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods manufacturing, where parts require precise shapes and structural integrity.
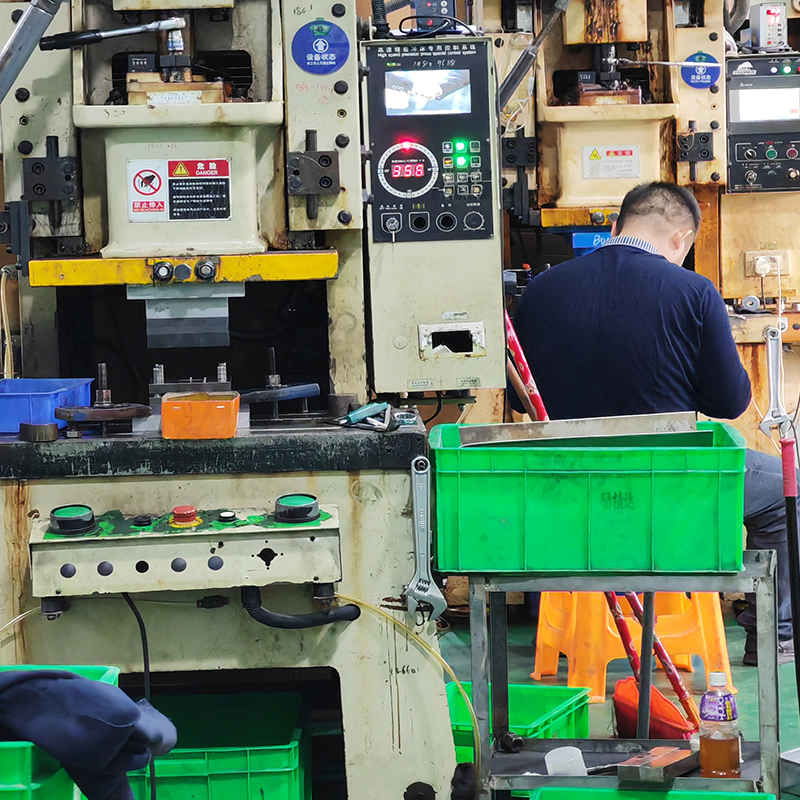

Common Stamping Operations:
- Punching:Cutting holes or shapes in metal.
- Blanking:Cutting out parts from a larger sheet.
- Embossing:Creating raised or recessed designs on the surface.
- Bending:Forming metal into angles or curves.
- Coining:Applying high-pressure to shape metal with fine detail.
What is Metal Punching?
Metal punching is a specialized subset of metal stamping, focused solely on creating holes or cutouts in sheet metal. It is typically performed using a punch press, where a punch tool is forced through a sheet of metal, creating precise holes or other cutout shapes. Unlike stamping, which may involve forming and shaping the entire piece of metal, punching is purely concerned with the removal of material to create voids or perforations.
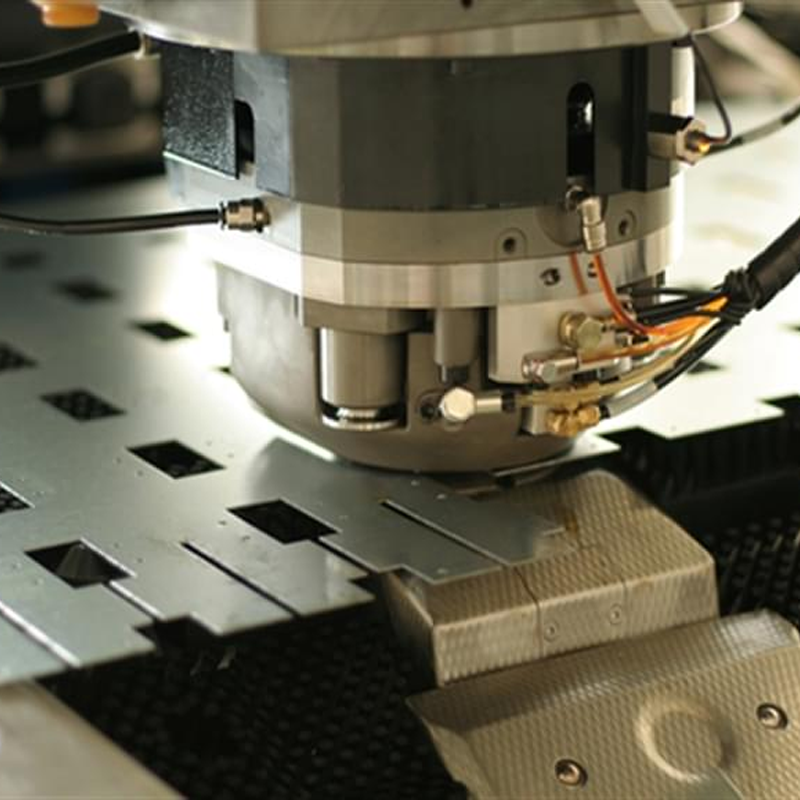

While punching is sometimes part of a larger stamping operation, it can also be performed as a standalone task, depending on the specific manufacturing requirements. It is commonly used for creating mounting holes, ventilation slots, and other perforations in a variety of products, including automotive panels, brackets, and circuit boards.
Common Punching Applications:
- Automotive:Mounting holes for brackets or support structures.
- Electronics:Perforated casings for ventilation or wiring.
- Appliances:Ventilation slots in appliance panels.
Comparing Metal Punching and Estampación Metálica
While metal punching and stamping both use press and die systems, the key difference lies in their respective functions. Metal stamping encompasses a wide range of metal forming operations, including punching, but also extends to processes like bending, embossing, and coining. Punching, on the other hand, focuses exclusively on creating holes and cutouts.

To make the comparison clearer, here is a table that summarizes the main differences between metal punching and metal stamping:
| Aspect | Metal Punching | Estampación Metálica |
| Primary Function | Creating holes or cutouts | Shaping metal into complex 3D structures or cutting sections |
| Material Thickness | 0.0036 – 0.5 inches | 0.0001 – 6 inches |
| Tools Used | Punch and die set | Heavy-duty stamping press |
| Setup Cost | $200 – $10,000 | $10,000 – $100,000 |
| Plazo de Entrega | Short, single-step operation | Longer due to multi-step operations |
| Material Waste | Higher, as slugs are created from punching | Lower, as many stamping operations don’t remove material |
| Applications | Perforating casings, creating mounting holes | Body panels, casings, surgical components, structural parts |
| Die Complexity | Simple, focused on cutting | Complex, involves multiple forming techniques |
Process Principles: Punching vs. Stamping
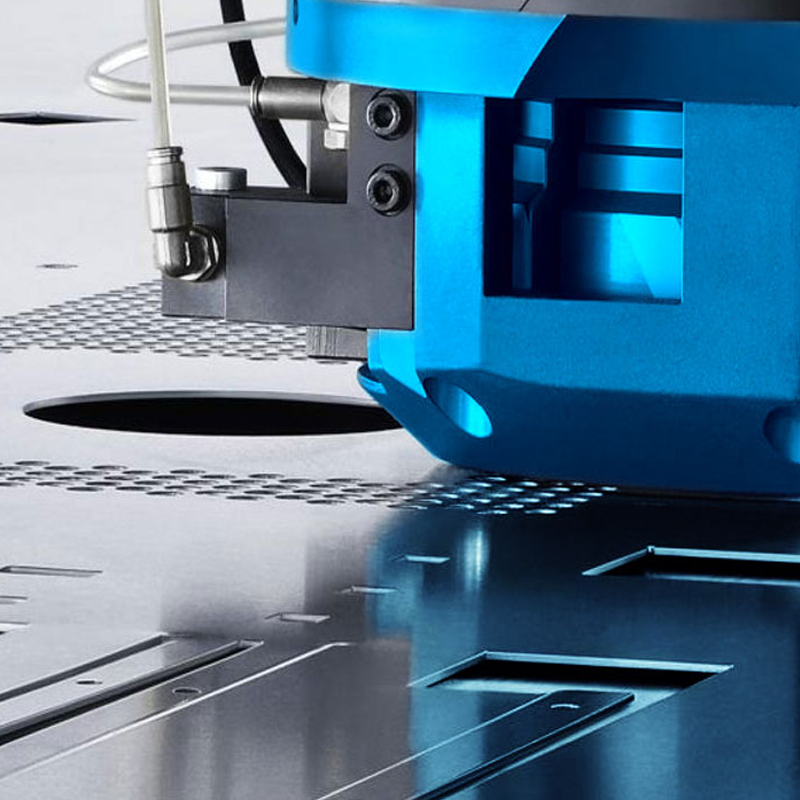
The working principle behind both punching and stamping involves the use of a press and die system. The press applies force to the die, which shapes or shears the material according to the design requirements. However, in stamping, the press is used to form the metal into 3D shapes, whereas in punching, the focus is solely on creating holes or cutouts.

Stamping often involves multiple operations, such as bending, blanking, and embossing, while punching is typically limited to cutting holes. This makes stamping more versatile, suitable for producing complex, multi-dimensional parts, while punching remains specialized for hole-making tasks.
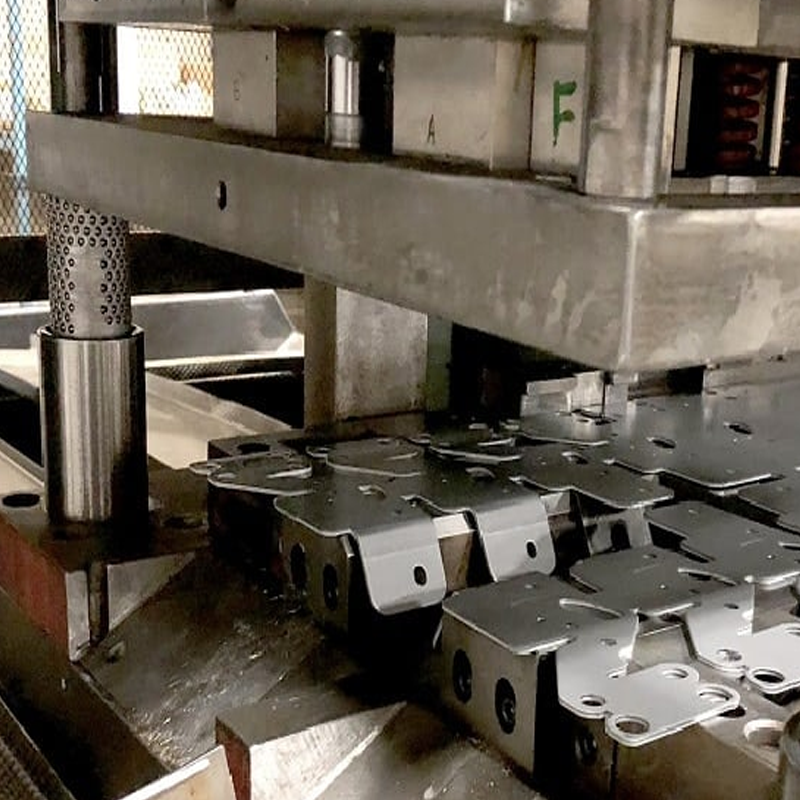
Material Thickness and Design Complexity
Both metal punching and stamping are generally suited for sheet metal applications, with thicknesses ranging from 0.0036 inches to 6 inches. However, stamping presses are capable of handling thicker materials and can form heavier gauges of metal. Some advanced stamping presses can even shape steel bars up to 3 inches thick.
While punching can handle materials as thin as 0.0036 inches, it is most effective on sheets that range from 0.5mm to 6mm thick. Punching is also less complex in terms of design, as it typically involves creating simple holes or cutouts. In contrast, stamping allows for more intricate designs and complex geometries, including multi-step processes that produce highly detailed, functional parts.
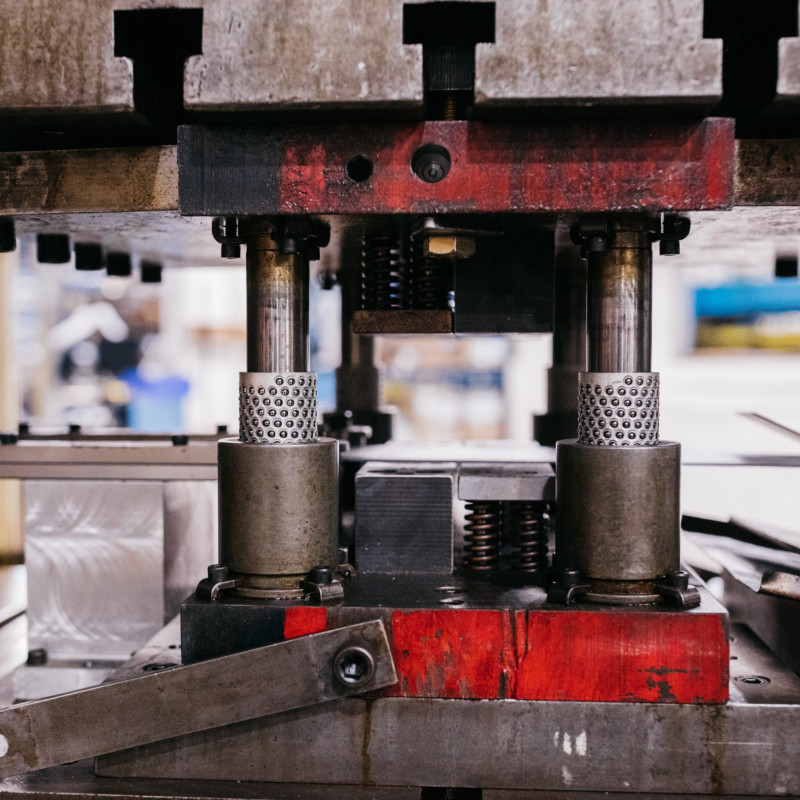

Equipment and Tooling
The equipment used in metal punching and stamping also varies in terms of complexity and cost. Punch presses are typically smaller and more compact, with a simpler design. They are ideal for high-speed operations that require precise hole placement but limited shaping. Many punch presses are equipped with turret tools that allow for quick changes between different punch sizes.
Stamping presses, on the other hand, are much larger and heavier-duty. These machines are designed to handle the significant forces required for complex metal forming. Stamping presses often come with larger beds to accommodate multiple dies, and they may be hydraulic or mechanical, depending on the type of force control required for the job.
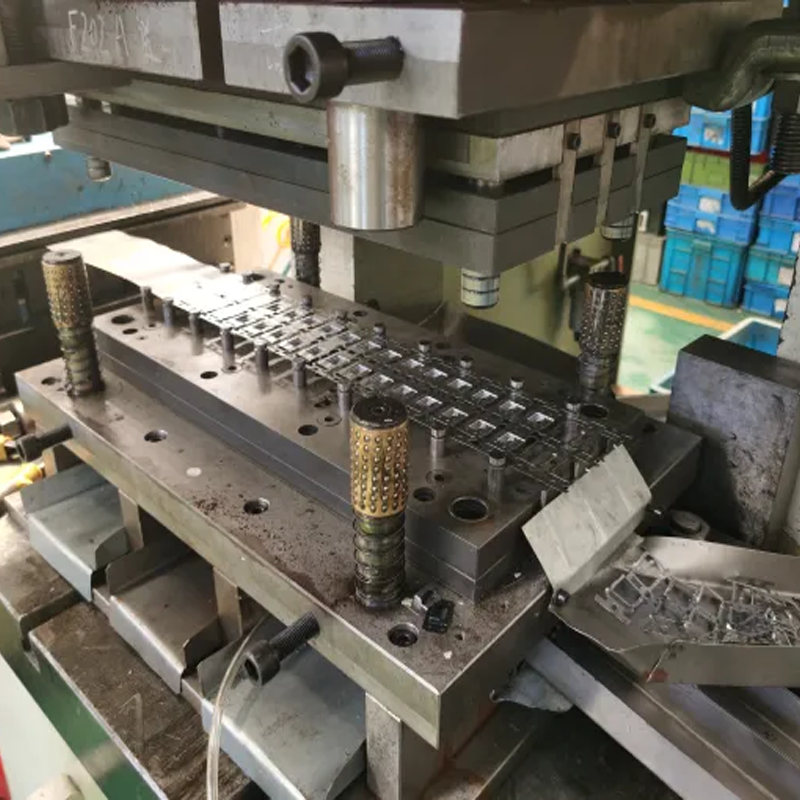

Cost Considerations
Punch presses are more cost-effective than stamping presses, especially for smaller-scale operations. The initial investment in a punch press is typically lower, and ongoing operational costs are relatively minimal. Punching is also faster than stamping, making it an economical choice for high-volume production of simple parts.
Stamping presses, however, involve higher setup and operational costs due to the complexity of the process and the heavier-duty machinery involved. Despite these higher costs, stamping is often more economical in the long run for large-scale production of intricate parts, as it reduces material waste and setup time over the course of a project.
Lead Time and Material Waste
The lead time for punching is generally shorter than stamping, as it is a single-step process that quickly creates holes in metal sheets. Stamping, by contrast, can involve multiple steps, which increases the overall lead time. However, stamping is more efficient when it comes to material usage. Punching creates waste in the form of slugs, while stamping often shapes the metal without removing significant material.
Applications of Punching and Stamping
The applications of punching and stamping are diverse and depend largely on the specific requirements of the project. Punching is ideal for applications that require precise holes or cutouts, such as ventilation slots or mounting holes. It is widely used in industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
Stamping, with its ability to form complex 3D shapes, is more suited for high-volume production of parts like body panels, structural components, and intricate housings. It is especially useful in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing.
How Plantmetal Can Help with Your Sheet Metal Fabrication Needs
At Plantmetal, we offer both metal punching and stamping services, providing high-quality solutions tailored to your specific manufacturing needs. Our team of experienced engineers and technicians works closely with clients to ensure that each project is completed efficiently, within budget, and to the highest standards of quality.
Whether you need simple punched holes or complex stamped parts, Plantmetal has the expertise and equipment to deliver exceptional results. Our state-of-the-art facilities and advanced tooling capabilities allow us to handle a wide range of materials and thicknesses, ensuring the success of every project.
For more information on how we can assist with your metal fabrication needs, contact us today! We look forward to helping you bring your designs to life with precision and expertise.