In the world of modern manufacturing, few tools are as essential as dies. These specialized tools are pivotal in shaping raw materials—such as metal, plastic, and composites—into complex, precise parts used across a wide array of industries. Whether you’re producing automotive components, consumer electronics, or industrial equipment, dies play a central role in ensuring consistency, accuracy, and efficiency in production. But what exactly are dies, how do they function, and why are they indispensable in high-volume manufacturing? This article explores the critical role of dies, the processes they enable, and the advantages they bring to manufacturing operations.
What Is a Die in Manufacturing?
At its core, a die is a custom-designed tool used to cut, shape, or form raw materials into specified shapes or sizes. Dies are used in conjunction with stamping presses, which apply substantial force to the material, pushing it into the die’s cavity to create the desired part. Dies are typically crafted to meet the unique specifications of the product being produced, enabling manufacturers to generate parts with high repeatability and precision. Dies are essential for producing everything from automotive components and appliances to medical devices and electronics enclosures.
The versatility of dies allows manufacturers to produce a broad range of products, all with consistent quality. Whether producing simple fasteners or complex, intricate parts, dies enable the high-volume production necessary for industries that demand both speed and accuracy.
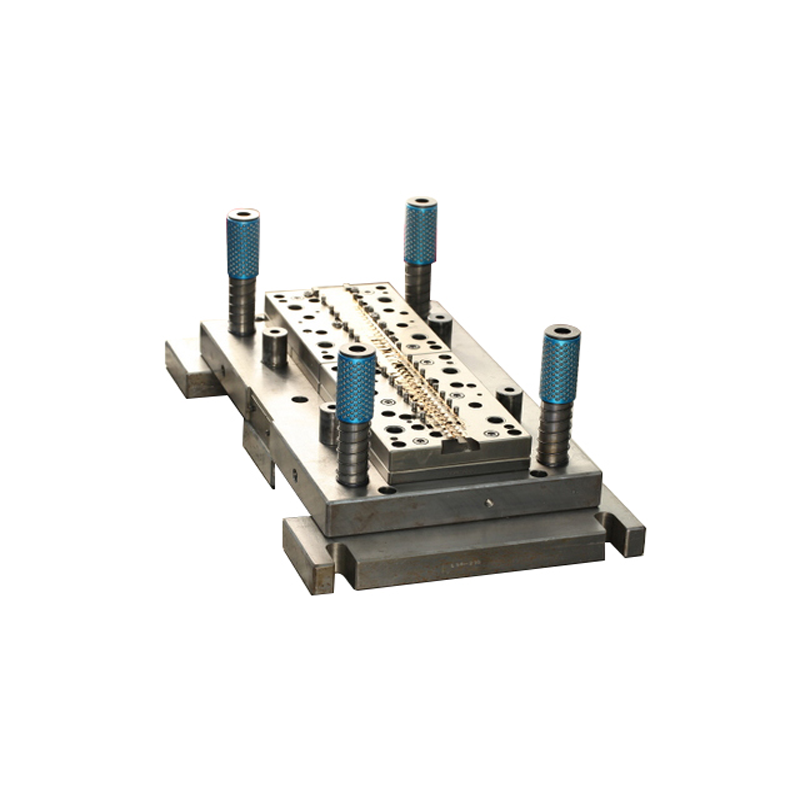
How Dies Operate in the Manufacturing Process
The process in which dies are employed is often called die stamping or die forming. Here’s how it works:
- Material Placement – A flat sheet of material, such as metal or plastic, is placed into a press.
- Pressing Action – The press applies a significant amount of force to the material, pressing it into the die’s cavity.
- Part Formation – The die’s cavity has the shape of the desired final part, so as the material is pressed in, it adopts that shape.
There are various operations that dies facilitate, each suited to specific manufacturing needs. Some common processes include:
– Blanking – Cutting a flat sheet of material into a basic, flat shape, which can then be further processed.
– Coining – Using high pressure to form intricate designs, logos, or embossed features onto the material.
– Deep Drawing – Shaping a flat material into a deep, hollow part, such as beverage cans or automotive body parts.

– Piercing and Punching – Creating holes or cutouts in the material, essential for components like bolts, screws, or electrical connectors.
– Forming – Shaping material into specific forms through bending or stretching, without cutting it.
These processes enable the creation of complex, high-precision parts that are integral to many industries.
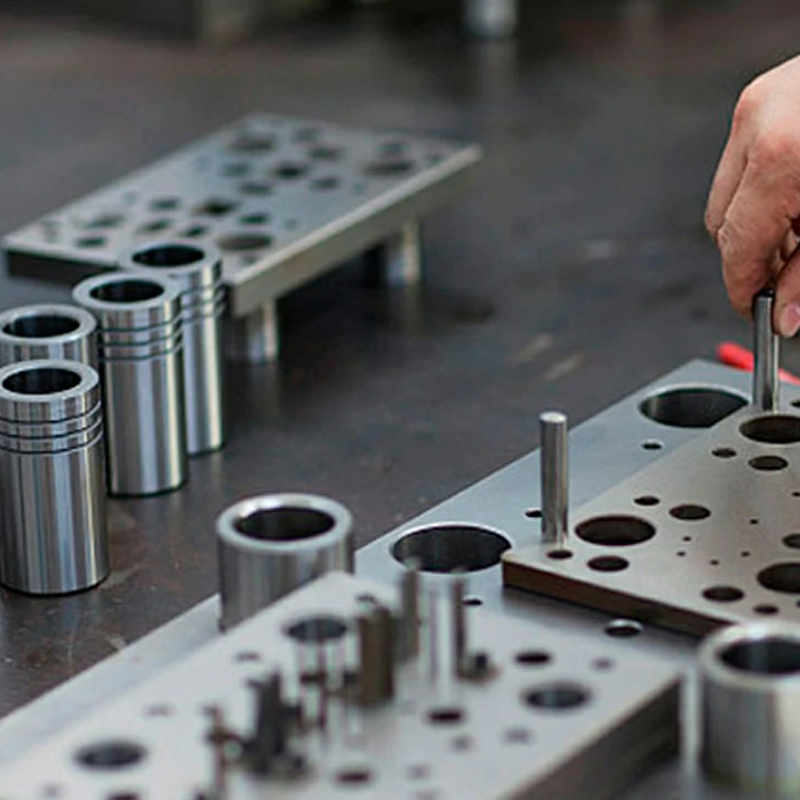
Components of a Die Set
A die set is an intricate assembly of parts that work together to form the final product. Each part plays a distinct role in ensuring the die functions correctly and produces parts with the required specifications. Key components include:
– Punch Plate – Holds the punch and guides it through the material during the forming process.
– Die Block – The heart of the die set, where the cavity is located.
– Blank Punch – The tool used to cut the raw material into a basic shape or blank.
– Pierce Punch – Used for making holes or specific cuts in the material.
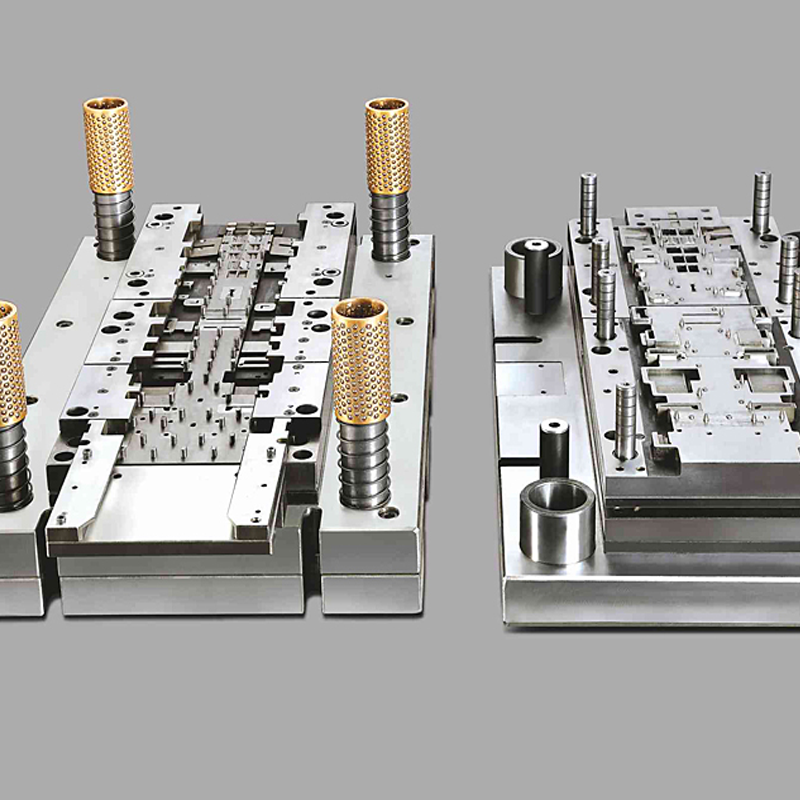
– Shank – The part of the die that attaches to the press.
– Pilot – Ensures the raw material is accurately aligned before entering the die.
– Stripper Plate – A tool that removes the formed part from the die once it’s complete.
Each component is carefully engineered to ensure high precision and longevity, making the entire die system vital to producing parts consistently.
Dies vs. Molds: Key Differences
While dies and molds are both used to shape materials, they are distinct in their operation and application:
– Molds – Molds are typically used in casting or injection molding processes, where material is poured into a hollow cavity and then solidified into the desired shape. Molds are ideal for materials like plastics and rubber.
– Dies – Dies use mechanical force to shape solid materials. Materials such as metal, plastic, or composite sheets are pressed into a die’s cavity to create the part. Dies are primarily used in stamping, cutting, and forming processes.
While both tools serve to shape materials, dies excel in high-volume, precision applications such as metal stamping and sheet metal forming, whereas molds are more suited to processes like casting and molding.
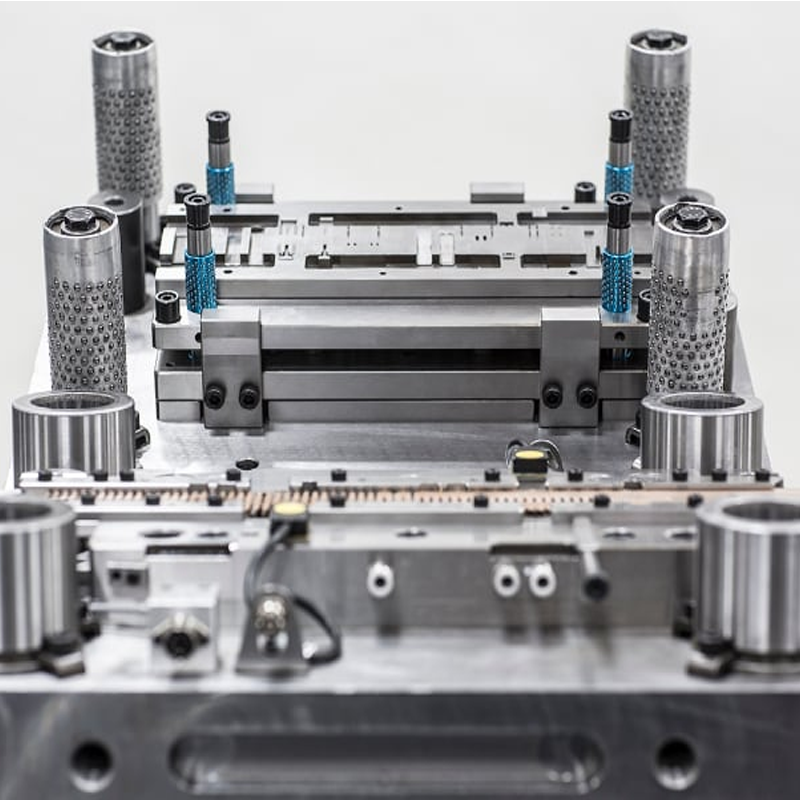
The Advantages of Dies in Manufacturing
Dies provide numerous benefits in manufacturing, especially for high-volume production. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Precision and Consistency – Dies are capable of producing parts with extreme precision, ensuring that every part meets exact specifications. This consistency is crucial in industries where even small deviations can lead to defects.
- High-Speed Production – Once a die is fabricated, it can be used repeatedly, allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities of parts quickly. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive manufacturing, where high-volume production is essential.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Although the initial investment in die tooling can be substantial, the long-term cost savings are significant. Dies reduce the need for extensive labor and minimize material waste, making them a highly cost-effective solution for large production runs.
- Complex Geometries – Dies are capable of producing intricate shapes and features, such as embossing or texturing, that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using other manufacturing methods.
- Reduced Lead Times – Once a die is in place, the lead time for producing parts is reduced significantly. This quick turnaround is a major advantage in industries where time-to-market is critical.
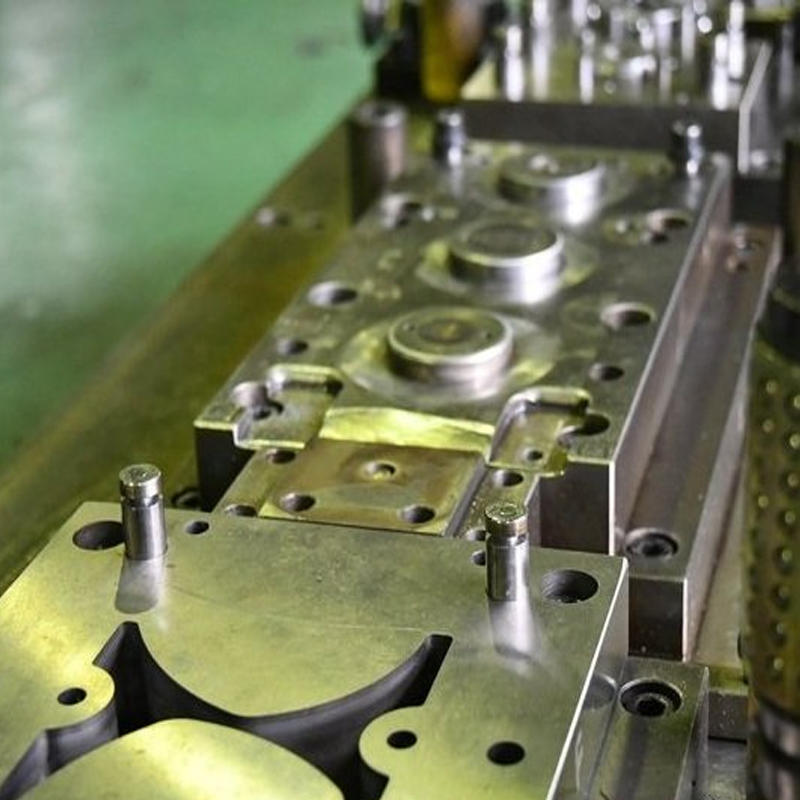

Applications of Dies Across Industries
Dies are used in a variety of manufacturing processes across multiple industries. Some key applications include:
– Automotive – In the automotive industry, dies are used to create everything from engine components to body panels, offering the precision needed for high-performance vehicles.
– Electronics – Dies are used to create small, complex parts for consumer electronics, ensuring both functional and aesthetic precision.
– Aerospace – The aerospace industry demands parts with tight tolerances and the ability to withstand extreme conditions, making dies an essential tool for producing critical components.
– Medical Devices – Precision is paramount in the medical field, and dies are used to create intricate parts for devices such as surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
Selecting the Right Die for Your Needs
Choosing the right die is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets your specifications. Here are several factors to consider when selecting a die for your manufacturing operation:
– Material Type – Make sure the die is compatible with the material you intend to work with, whether it’s metal, plastic, or composite.
– Complexity of the Part – Some parts require more intricate die designs, so understanding the complexity of the part will help you determine which die process is best suited for your needs.
– Volume of Production – The size of your production run will influence the type of die you choose. For large volumes, a custom die may be the most cost-effective solution.
– Precision Requirements – If your part requires extremely tight tolerances, you may need to invest in a higher-precision die, such as a servo-driven press system.

Conclusion
Dies are essential tools for producing high-precision parts efficiently and cost-effectively. They enable manufacturers to create complex components quickly, with minimal waste and high consistency. Whether you’re producing automotive parts, electronics enclosures, or custom components, selecting the right die is crucial to achieving the desired quality and efficiency.
If you’re looking to integrate die stamping into your manufacturing process or need guidance on selecting the best die for your operation, we’re here to help. Our expert team can walk you through the process and ensure that you get the highest quality parts produced at optimal efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your die manufacturing needs or ask any questions you may have—we’re ready to assist you in optimizing your production processes!




