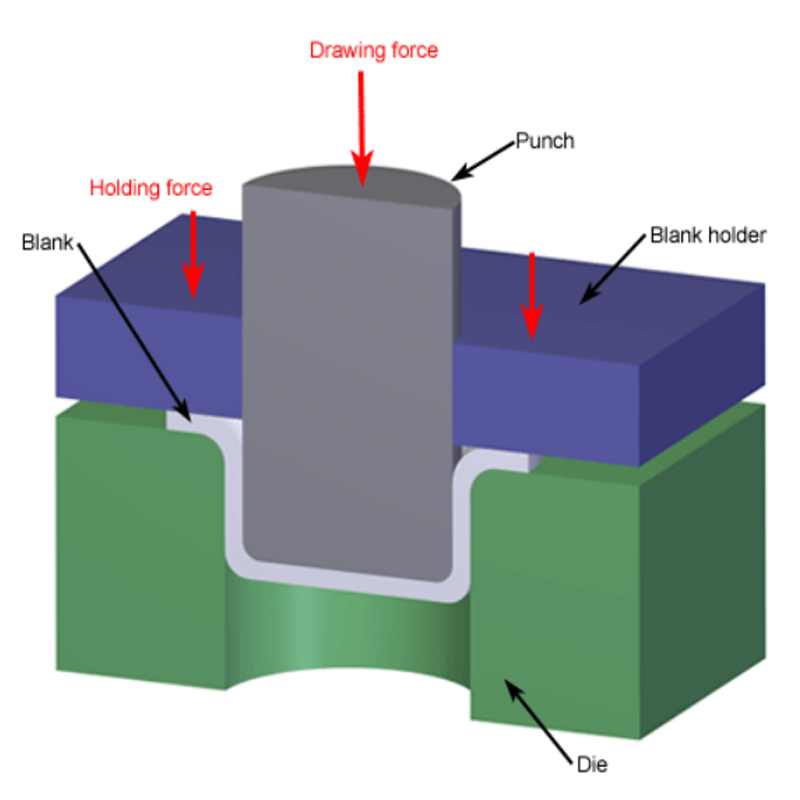
Deep drawing is an advanced metalworking technique that effectively converts flat metal sheets into complex three-dimensional components. The process begins by placing a sheet of metal over a die, where a punch applies pressure to push the metal into the die cavity. This application of force causes the metal to undergo plastic deformation, allowing it to take on the precise shape of the die. With its ability to create a wide variety of shapes and profiles, deep drawing has become a crucial method in many manufacturing sectors, showcasing its versatility and efficiency in producing intricate designs.
Advantages of Deep Drawing
Seamless Fabrication: Deep drawing allows for the formation of metal sheets into complex shapes without the need for joints or seams, resulting in stronger, more durable components.
Enhanced Production Efficiency: This method enables the rapid creation of intricate geometries, facilitating high-volume production and significantly boosting overall manufacturing efficiency.
Material Optimization: By effectively utilizing flat sheets, deep drawing minimizes waste, reducing scrap material and lowering raw material costs.

Improved Material Characteristics: The process enhances the mechanical properties of the material through plastic deformation, resulting in components that are both stronger and more resilient.
Cost Efficiency: Compared to other manufacturing techniques, deep drawing is time- and cost-effective, translating to lower production costs due to its high productivity, material savings, and reduced labor requirements.
Versatility Across Industries: Deep drawing can produce a wide range of shapes and sizes, making it suitable for various sectors, including automotive and household appliance manufacturing.
Consistency and Precision: This process ensures uniformity and dimensional accuracy, delivering consistent quality across large production runs that meet exact specifications.
Reduced Need for Post-Processing: Parts created through deep drawing typically require less finishing or secondary operations, saving time and resources in the overall manufacturing process.
Deep Drawing Process
Material Selection and Preparation: The selection of the appropriate material involves considering performance requirements and desired properties, ensuring that the chosen material meets specifications and is free from defects.
Blank Cutting: The selected material is cut into blank shapes using shearing or laser cutting techniques, tailored to the design specifications.
Blank Cleaning and Surface Preparation: Thorough cleaning of the blank removes contaminants, while surface preparation methods such as degreasing enhance adhesion and help prevent defects.
Tooling Setup: The die and punch assembly is configured according to the dimensions and specifications of the part being produced.

Lubrication: Applying lubricants to the blank and tooling surfaces reduces friction, improving material flow during the drawing process.
Loading the Blank: The prepared blank is positioned in the die cavity, ready for the drawing operation.
Drawing Process: The press applies force to press the blank into the die cavity, deforming the material to create the desired shape.
Trimming: Excess material is trimmed from the final part to achieve precise dimensions and eliminate irregularities.
Post-Forming Operations (Optional): Depending on technical requirements, additional processes such as hole punching, bending, or welding may be performed.
Quality Control: Various quality assurance methods are implemented to assess the components’ quality and ensure compliance with production standards.
Factors Affecting Deep Drawing
Material Properties: The characteristics of the selected material significantly influence the outcomes of deep drawing. Materials with high ductility, such as stainless steel and aluminum, are ideal, whereas harder materials may suffer from cracking or tearing.
Material Thickness: Thinner materials are easier to deform, while thicker materials require greater force, increasing the risk of damage such as wrinkling.
Die and Punch Design: Effective design of the die and punch is crucial. Smooth transitions and proper radii help avoid defects and ensure effective forming.
Lubrication: Proper lubrication minimizes friction between the die and metal, enhancing formability and surface finish while also prolonging tool life.

Blank Holder Pressure: Correct application of pressure on the blank holder is essential for controlling material flow and preventing wrinkling or tearing.
Draw Ratio: The draw ratio, defined as the diameter of the final part relative to that of the blank, influences the severity of deformation. Higher draw ratios can increase the risk of material rupture.
Temperature: The temperature of the material can impact flow and formability. Heating the material can lower tensile strength and enhance flexibility, making deformation easier.
Surface Finish: The finish of both the material and tooling affects friction and material flow during deep drawing. Polished surfaces contribute to reduced friction and improved surface quality.
Applications of Deep Drawing
Automotive Industry: Deep drawing is utilized to manufacture car body panels and engine components, enhancing vehicle durability and precision.
Appliances: Metal parts for appliances like refrigerators and washing machines are produced through deep drawing, improving reliability and performance.
Electronics: This technique creates metal covers for electronic devices, ensuring safety and aesthetic appeal in consumer electronics.
Cookware and Kitchenware: Deep drawing is employed to manufacture robust and heat-resistant kitchen items such as molds, pans, and utensils.

Medical Devices: Deep drawing produces parts for medical equipment and implants, ensuring reliability and sterility in healthcare environments.
Aerospace: The aerospace sector benefits from tailor-made components created through deep drawing, ensuring lightweight and high-performance structures.
Packaging: Deep drawing is used to manufacture metal containers and lids for food and beverages, ensuring freshness and convenience in storage and transport.
Construction: This process is often applied in fabricating construction materials that enhance the strength and stability of building structures.
Consumer Goods: A wide variety of consumer products are developed using deep drawing, ensuring they are both functional and visually appealing.
If you are looking to customize metal components using deep drawing techniques, we are here to provide expert guidance and solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our team can help you explore the possibilities and achieve the highest quality results for your projects.