Metal stamping is a widely used manufacturing process that involves shaping metal sheets into various forms using specialized dies and presses. As companies scale up production, they often face the decision of when to invest in dedicated tooling for their metal stamping needs. At Plantmetal, we understand that tooling decisions are complex and need to balance cost, production volume, part complexity, and overall goals. Whether you’re looking for a prototype or aiming for large-scale manufacturing, this guide will help you navigate the critical considerations involved in determining the right time to invest in a metal stamping tool for your production needs.
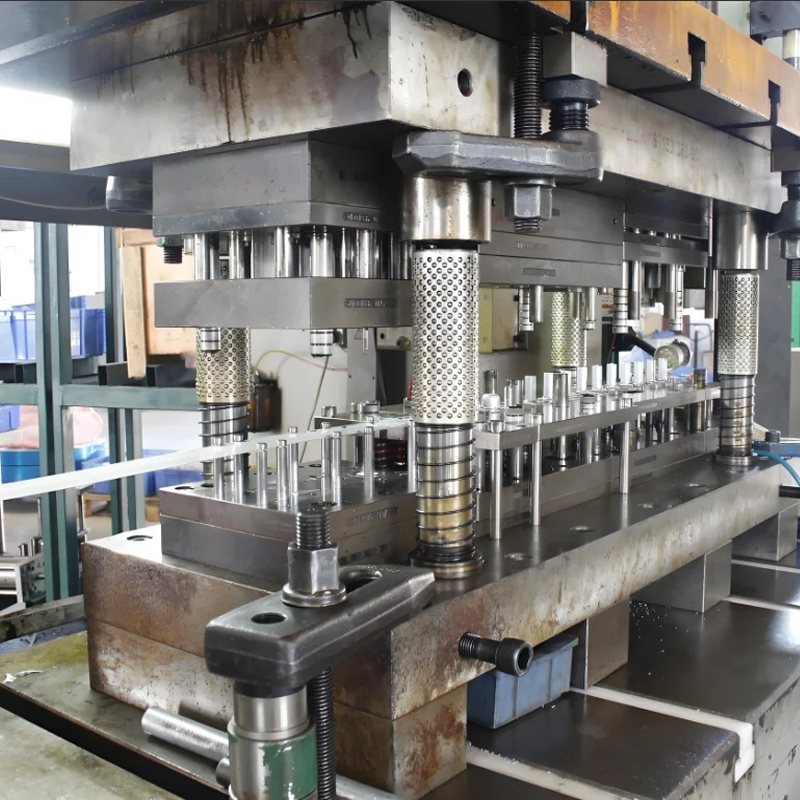
Understanding Metal Stamping Tools
Before we dive into the specifics of low, mid, and high-volume production, it’s essential to understand the various types of tools used in metal stamping:
- Single-Operation Dies: These tools are used for basic operations like cutting, punching, and blanking. They are generally simpler and ideal for straightforward tasks.
- Progressive Dies: These dies are more advanced, capable of handling multiple operations in a single cycle as the material moves through the die. This process increases efficiency for certain types of work.
- Transfer Dies: For complex parts with multiple steps, transfer dies move the part through several stages within the die, making them ideal for intricate designs that require precise handling.
Choosing the right tooling involves weighing the cost against production needs. The decision depends on factors such as the volume of production, the complexity of the parts being made, and the need for precision.
Low-Volume Production: When Cost Efficiency Takes Priority
Характеристики:
– Volume: Less than 10,000 parts
– Tooling Costs: High relative to the low production volume
– Production Goals: Often for prototypes, test runs, or limited production batches
Tooling Considerations:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: For low-volume production, investing in high-quality, durable tools may not be cost-effective. The initial investment in a custom die can be substantial, and with only a small number of parts to produce, the cost per part can be prohibitively high. In these cases, it’s essential to evaluate whether the tooling costs are justifiable.
- Alternative Approaches:
– Soft Tooling: For shorter runs, manufacturers may consider using softer materials, such as zinc-based alloys or non-heat-treated steel. These materials are more affordable and suitable for prototypes or test runs. While they lack the precision and longevity of hardened steel, they can often deliver acceptable results for low-volume needs.
– Manual or Semi-Automatic Tools: Manual or semi-automatic dies can be faster and cheaper to produce. For low-volume runs, where precision is less critical, these tools may be an efficient and cost-effective option.

– 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping: In some cases, 3D printing can be an effective alternative for low-volume production. While not suitable for high-stress or high-precision applications, 3D printed dies can be a cost-efficient way to test product designs in very small quantities.
- Tool Design: Simplifying the design of tooling for low-volume production can help reduce initial costs. By focusing on only the essential features of the part, manufacturers can streamline the design process and keep costs manageable.
Mid-Volume Production: Balancing Durability and Efficiency
Характеристики:
– Volume: Between 10,000 and 100,000 parts
– Tooling Costs: Substantial but spread over a larger production run
– Production Goals: Often used for moderate-sized runs, test phases, or market launches
Tooling Considerations:
- Cost Efficiency: As production volumes increase, investing in more durable and precise tooling becomes more cost-effective. The cost per part goes down as the initial tooling investment is spread over more parts. This makes it easier to justify spending on higher-quality tools that will improve efficiency and reduce defects.
- Tooling Material: For mid-volume production, hardened steel tools are generally the best option. These tools offer a good balance of durability, precision, and cost-effectiveness. While the initial investment is higher, they last longer and produce better-quality parts over time, making them ideal for moderate production runs.
- Tooling Complexity: As production needs grow, more complex dies like progressive or transfer dies may be necessary. These tools can perform multiple operations in a single pass, which boosts efficiency and accuracy. Investing in advanced dies can help reduce cycle time and improve part quality for mid-volume runs.
- Maintenance: As tooling becomes more complex and production volumes increase, regular maintenance becomes critical. Routine maintenance and inspections are necessary to ensure that tools continue to perform at peak efficiency and produce high-quality parts throughout their lifecycle.

High-Volume Production: Maximizing Efficiency and Precision
Характеристики:
– Volume: More than 100,000 parts
– Tooling Costs: High, but cost per part is significantly reduced due to large production runs
– Production Goals: Large-scale manufacturing, cost efficiency, and high precision
Tooling Considerations:
- Investment Justification: For high-volume production, the initial tooling costs are substantial, but they are justified by the extremely low cost per part. At this scale, maximizing efficiency and maintaining consistent quality is crucial. The focus shifts from minimizing initial costs to optimizing long-term production capabilities.
- Tooling Material: Hardened steel is the material of choice for high-volume production. These tools are designed to handle large quantities of parts while maintaining precision and durability. At this scale, investing in high-quality tooling ensures that parts are produced consistently and that the tooling lasts longer.
- Tooling Complexity: High-volume production often requires advanced dies that can handle multiple stations or complex operations. Progressive and transfer dies are essential for maintaining high throughput and accuracy. These complex tools allow manufacturers to meet the demands of large-scale production while ensuring that parts remain consistent and high-quality.
- Automation: To maximize efficiency, many high-volume stamping operations integrate automation into their processes. Automation helps reduce labor costs, increase throughput, and improve part consistency, all of which contribute to cost savings and operational efficiency in high-volume environments.
- Maintenance and Quality Control: As with mid-volume production, regular maintenance and stringent quality control procedures are vital for high-volume operations. Continuous monitoring and preventive maintenance are necessary to prevent production downtimes and ensure that parts consistently meet customer specifications.

Making the Right Decision
When deciding whether to invest in tooling for your metal stamping project, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Production Volume:
– For low volumes, alternative manufacturing methods or soft tooling can provide a more cost-effective solution.
– Mid-volume runs justify more durable tooling, which improves efficiency and part quality.
– For high volumes, investing in advanced, durable tooling is essential for maximizing efficiency and maintaining part consistency.
- Cost Considerations: Evaluate the cost of tooling relative to the production volume and compare it to alternative manufacturing methods. The cost per part will decrease as the production volume increases, which makes investing in tooling more viable at mid and high volumes.
- Part Complexity: If your parts are complex, it may be worth investing in advanced tooling, particularly at mid to high production volumes. Complex parts may require multiple operations that are best handled by progressive or transfer dies.
- Production Goals: Consider your production goals—whether it’s for prototyping, small runs, or large-scale manufacturing—and choose your tooling accordingly. Aligning tooling decisions with your production goals will ensure that the process is both cost-effective and efficient.

Conclusion
At Plantmetal, we have over two decades of experience in providing high-quality, precision metal stampings and assemblies. Since our inception in 1998, we’ve become a trusted partner for companies in the United States, offering a wide range of capabilities, including forming, stamping, deep drawing, machining, assembly, and value-added operations. Whether your next project involves progressive die stamping, deep drawing, or precision machining, we have the expertise and state-of-the-art equipment to meet your needs.
By carefully considering the factors outlined in this guide and working with a trusted partner like Plantmetal, you can make an informed decision about when and how to invest in tooling for your metal stamping project, ensuring that your production is cost-effective, efficient, and meets the highest standards of quality. If you have questions or need assistance with your next project, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at Plantmetal—we’re here to help you achieve your manufacturing goals.




