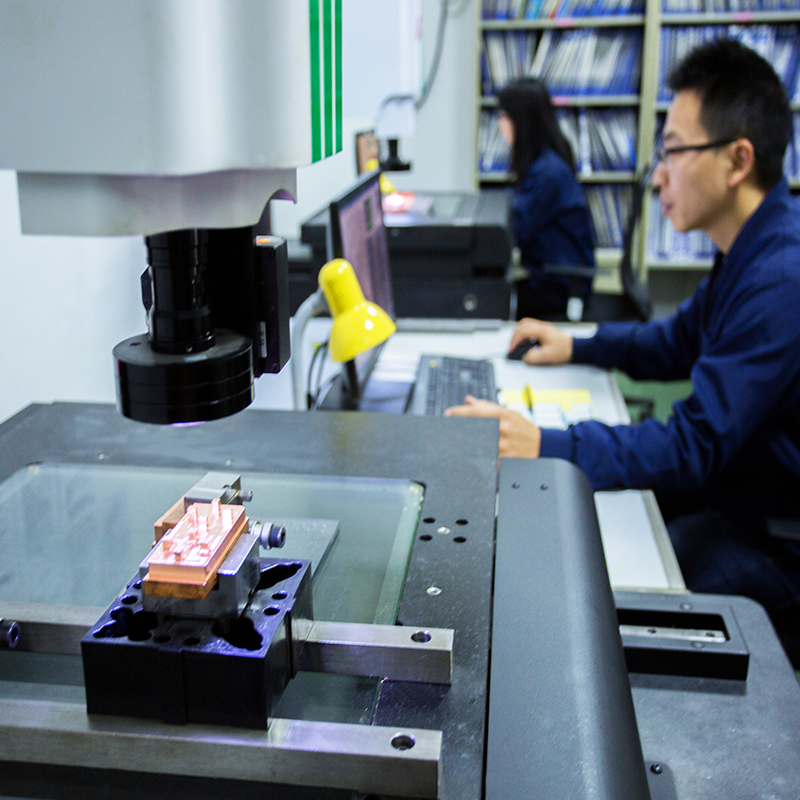
Molds are essential tools used in a wide range of industries to shape materials into specific forms. Whether for manufacturing plastic components, metal parts, or other materials, molds are designed and engineered to meet precise requirements. At Plantmetal, we specialize in producing high-quality molds for various applications, including metal stamping, that deliver exceptional performance and reliability. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what molds are, the key components that make up a mold, and the mold-making process.
What Is a Mold?
A mold is a rigid tool or frame used in various manufacturing processes to shape malleable materials, turning them into a desired form. Just like a template, a mold is created to replicate a specific design across multiple units. The materials used in mold production can vary depending on the application, with common materials including gypsum (plaster), resin, metals (such as bronze, aluminum, lead, silver, and gold), and cast rubber. Molds are critical in ensuring that products are manufactured consistently, accurately, and with high quality.
Key Components of a Mold
A mold used in manufacturing typically consists of several essential components. Each component plays a vital role in shaping the material and ensuring the final product is of the highest quality. While the specific components can vary depending on the type of mold and the manufacturing process, here are some of the most common parts of a mold:
– Cavity: The cavity is the hollow space within the mold where the material is poured, injected, or compressed to form the desired product. It defines the final shape and dimensions of the part being produced.
– Core: For molds with intricate shapes or undercuts, a core is used. The core forms the internal features of the part and fits inside the cavity. Together with the cavity, the core ensures the product is formed precisely according to design specifications.
– Runner System: In injection molding, the runner system guides the molten material from the injection unit into the cavity. This system typically includes a sprue (the entry point), runners (channels that direct material), and gates (where material enters the cavity).
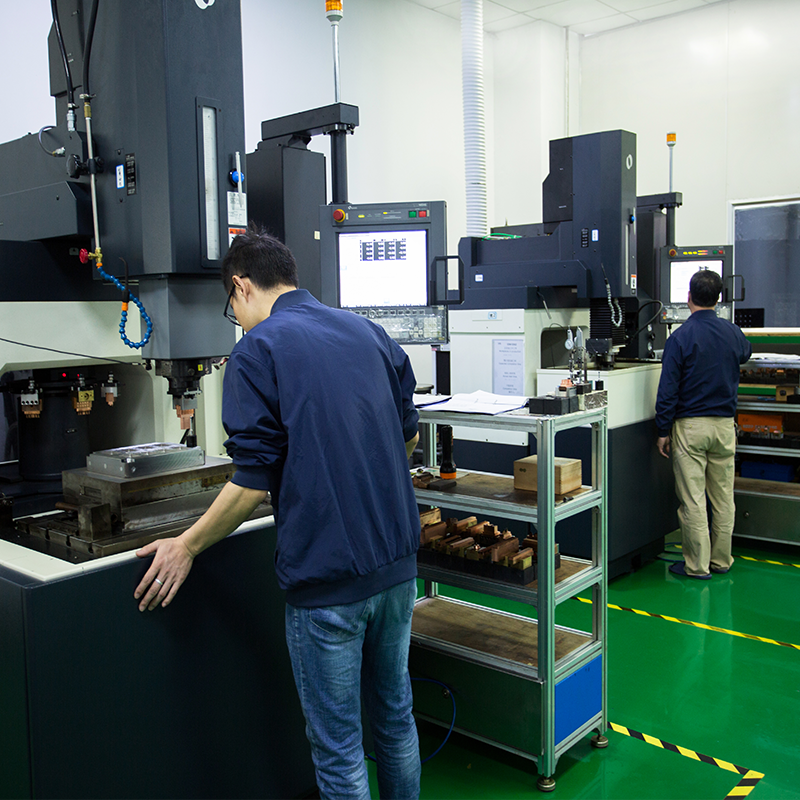

– Ejector Pins: Ejector pins are responsible for pushing the molded part out of the mold once it has cooled and solidified. These pins are typically located on the side of the mold opposite the cavity and ensure the easy removal of the finished part.
– Cooling Channels: Cooling channels are integrated into the mold to regulate its temperature during the molding process. Proper cooling is essential to maintain the consistency of the material and avoid issues such as warping or deformation.
– Venting System: Vents or venting systems allow air and gases to escape from the cavity as the material flows in. This is crucial for preventing defects such as air traps or incomplete filling.
– Slide or Lifter: Slides or lifters are mechanisms used in molds to create undercuts or complex shapes that may not be easily released from a simple two-part mold. These components help facilitate the ejection process.
– Cavity Inserts: Interchangeable cavity inserts allow for flexibility in mold design. These inserts enable the production of different product designs without needing to build a completely new mold, making them a cost-effective solution for product variation.
– Alignment Pins and Bushings: Alignment pins and bushings ensure that the mold halves (typically the cavity and core) align accurately when closed, guaranteeing dimensional precision in the final product.
– Mold Base: The mold base serves as the foundation for the entire mold assembly. It provides structural support and includes features for alignment and attachment of the core and cavity.
– Gate Inserts: In injection molding, gate inserts control the size and location of the entry point for molten material, ensuring smooth filling and uniform material flow.
These are some of the core components found in molds used in various manufacturing processes, including metal stamping. The specific composition and complexity of a mold will depend on the application and the desired product features.
The Mold-Making Process
Creating a mold involves a series of precise steps to ensure that it meets both design specifications and performance requirements. Below, we outline the general steps involved in the mold-making process:
- Product Design: The process begins with product designers creating detailed 3D CAD (computer-aided design) models of the part to be produced. These models are used as the blueprint for the mold.
- Conceptual Mold Design: Mold engineers and designers will create a conceptual mold design based on the product model. This includes determining the type of mold required (e.g., injection mold, die-cast mold, or metal stamping mold), as well as its basic structure.
- Precision Dimensioning: The dimensions of the mold are finalized, including the number of cavities (if multiple parts need to be produced simultaneously), the gating system, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms.
- Material Selection: The material for the production mold is chosen based on factors such as the expected number of cycles, the material being molded, and overall durability. Steel, aluminum, and various alloys are common choices for mold construction.
- Machining Techniques: The mold is then machined using techniques such as milling, turning, grinding, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). These techniques are used to create the mold’s cavities, inserts, and cooling channels.
- Assembly: Once all the individual components are fabricated, they are assembled to form the mold. This may involve bolting, welding, or clamping the core, cavity, and other components together.
- Surface Treatment: After assembly, the mold may undergo surface treatments to enhance durability, improve release properties, and reduce friction during the molding process.
- Testing and Quality Control: Before the mold enters full-scale production, it is rigorously tested and inspected to ensure it meets the required specifications. Any necessary adjustments are made to optimize performance.
- Production: Once testing and quality control are complete, the mold is ready for full-scale production, where it will be used to create the final product.
Why Choose Plantmetal for Your Mold-Making Needs?
At Plantmetal, we pride ourselves on delivering high-quality molds designed to meet the specific needs of our clients across a variety of industries, including metal stamping. Our experienced engineers and advanced manufacturing processes ensure that each mold is precisely crafted to produce the highest quality products. Whether you require a custom mold for injection molding, die-casting, or metal stamping, our team is here to provide expert guidance and unparalleled craftsmanship.
We are committed to excellence and customer satisfaction, and we stand by our work with stringent quality control measures, ensuring that every mold we create meets industry standards for durability, accuracy, and performance.
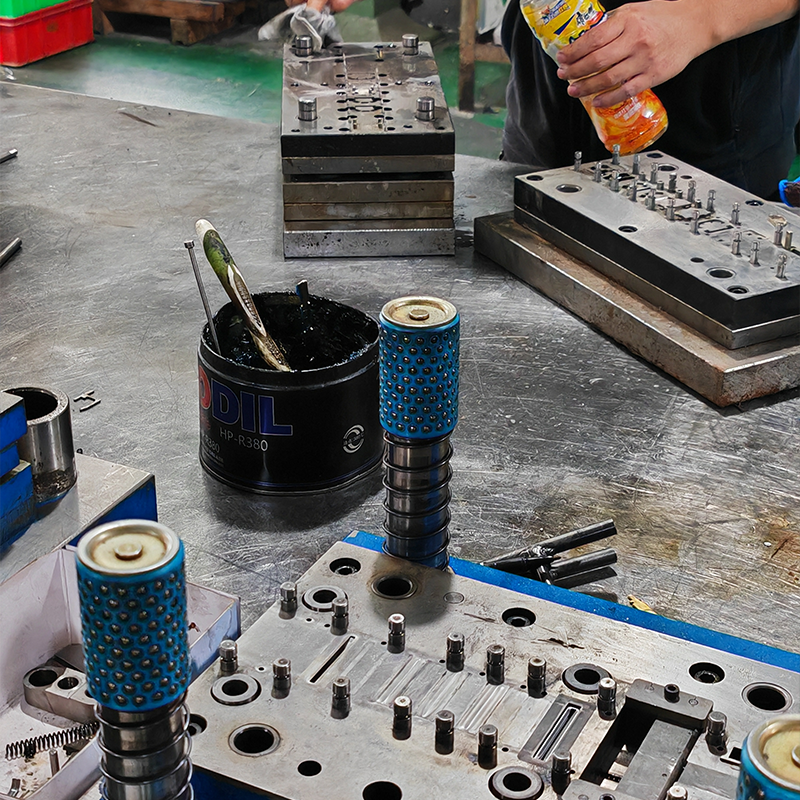

If you would like to learn more about our mold-making capabilities or inquire about our services, we invite you to visit our website. For a free, no-obligation quote, feel free to contact us directly. We look forward to helping you bring your product designs to life with precision and reliability.
By partnering with Plantmetal, you can be confident that your molds will be crafted to the highest standards, ensuring optimal performance and long-term success in your manufacturing processes.




